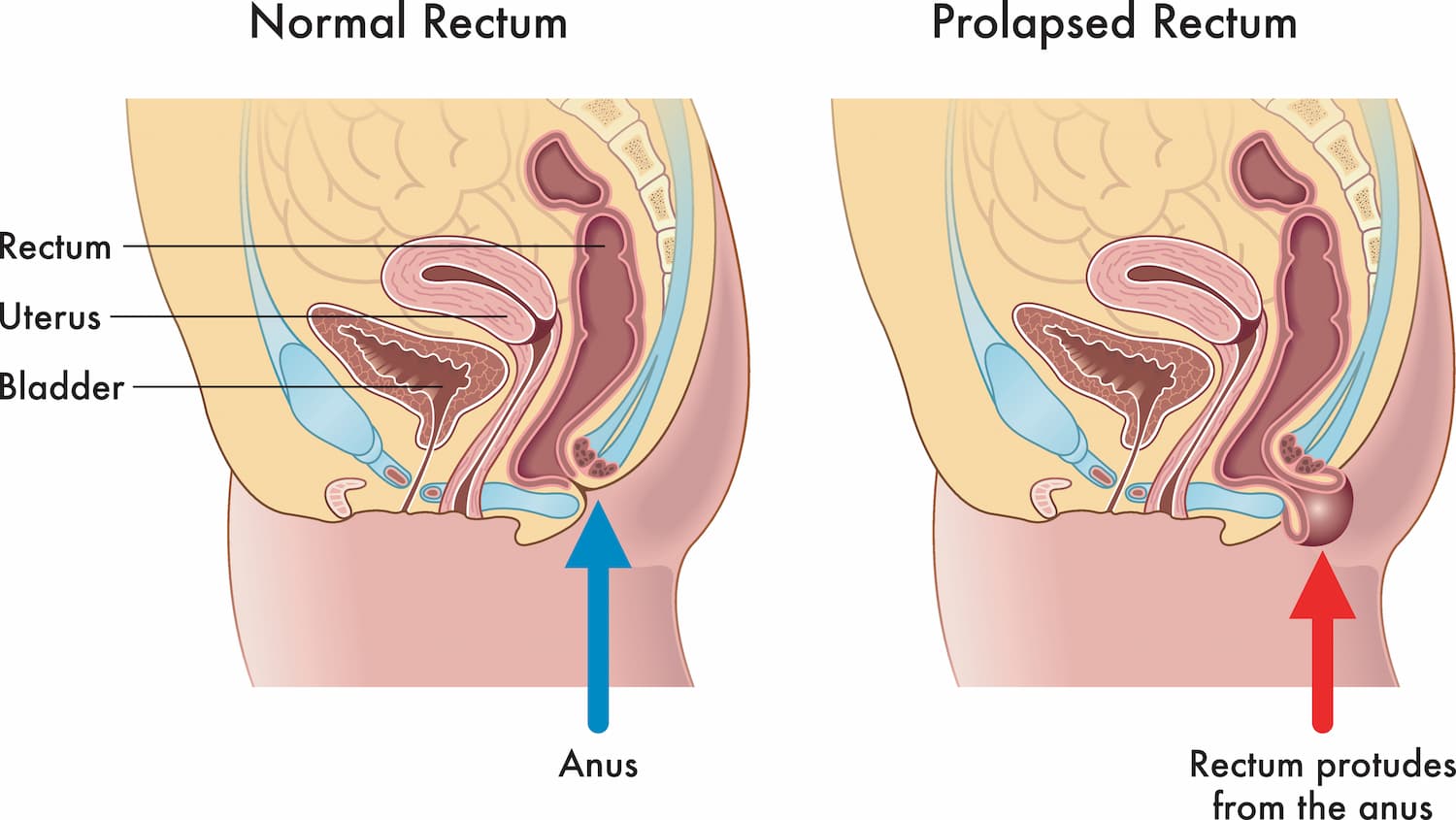
What is a Rectal Prolapse?
Rectal prolapse occurs when the rectum, the last part of the large intestine, protrudes from the anus. This protrusion can vary in severity and may involve different layers of the rectal wall. This can manifest as a partial prolapse, where only the rectal lining is involved, or a complete prolapse, where the entire rectal wall extends outside the body.
Rectal Prolaplse is a very distressing condition and can result in bleeding, pain, loss of control and social isolation. At Midlands Colorectal, we have particular interest and expertise in treating this condition with excellent results. When we see you in clinic we will take a full history and examine you. we will do a rigid sigmoidoscopy in clinic and may recommend that you have a longer camera examination – either flexible sigmoidoscopy or a colonoscopy. Following all your investigations We will discuss surgical management of the condition with you.
Surgery usually involves a general anaesthetic (being put to sleep) but may be done by spinal anaesthetic where you are awake. You can expect to stay in hospital for a day or two.
A number of procedures and approaches are available to treat this problem and we will discuss the best option for you.
What Causes Rectal Prolapse?
Rectal prolapse can be attributed to various factors, including:
Weakened Pelvic Floor Muscles:
The pelvic floor muscles support the rectum and other pelvic organs. Weakness in these muscles can lead to the descent of the rectum.
Age
The risk of rectal prolapse increases with age, particularly in individuals over 50.
Chronic Constipation
Straining during bowel movements, often associated with chronic constipation, can weaken the pelvic floor and contribute to prolapse.
Childbirth
In women, the stress and trauma of childbirth, especially multiple pregnancies, can increase the risk of pelvic floor disorders, including rectal prolapse.
Connective Tissue Disorders
Conditions that affect the strength and integrity of connective tissues may contribute to the development of rectal prolapse.
Understanding these causes helps in tailoring treatment plans and preventive strategies.
What Are the Different Types of Rectal Prolapse?
Rectal prolapse is diverse and can be classified into various types:
Full-Thickness (Complete) Prolapse
In this type, the entire thickness of the rectal wall protrudes through the anus. This often results in a noticeable bulge or mass outside the body.
Mucosal Prolapse
Mucosal prolapse involves the inner lining of the rectum (mucosa) protruding through the anus. This type may not present as a significant external bulge.
Internal or Occult Prolapse
Also known as internal intussusception, this type involves a folding or collapsing of the rectum without external protrusion. It may not be as visibly apparent but can still cause symptoms.
What Are the Symptoms of Rectal Prolapse?
Rectal prolapse can manifest with a variety of symptoms, and the severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the type and extent of the prolapse. Here are the key symptoms associated with rectal prolapse:
Visible Bulge or Protrusion
One of the hallmark signs of rectal prolapse is the presence of a visible bulge or mass that protrudes through the anus. This may occur during bowel movements or persist throughout the day.
Difficulty with Bowel Movements
Individuals with rectal prolapse often experience difficulty during bowel movements. This can include straining, a feeling of incomplete evacuation, or the need to manually assist in returning the rectum to its normal position.
Incontinence
Rectal prolapse can lead to difficulties in controlling bowel movements, resulting in faecal incontinence. Individuals may experience leakage of gas, liquid stool, or solid stool.
Discomfort or Pain
Patients with rectal prolapse may report discomfort or pain in the rectal area. This discomfort can be exacerbated during bowel movements or while the prolapsed tissue is outside the body.
Bleeding
In some cases, individuals with rectal prolapse may experience bleeding, especially if the prolapsed tissue becomes irritated or ulcerated. This can lead to visible blood on toilet paper or in the stool.
Feeling of Heaviness or Fullness
Some individuals describe a constant sensation of heaviness or fullness in the rectal area, even when the prolapsed tissue is not visibly protruding.
Urinary Symptoms
Rectal prolapse can sometimes be associated with urinary symptoms, such as difficulty emptying the bladder completely or an increased frequency of urinary tract infections.
Backache or Pelvic Pain
Chronic rectal prolapse may contribute to backache or pelvic pain due to the strain on pelvic structures.
It's important to note that symptoms can be intermittent, and individuals may not experience all of these symptoms. Additionally, the symptoms of rectal prolapse can be mistaken for other gastrointestinal or pelvic floor disorders, highlighting the importance of seeking medical evaluation for a proper diagnosis.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is crucial to seek prompt medical attention. A healthcare provider, such as those at Midlands Colorectal, can conduct a thorough examination, including a medical history, physical examination, and potentially imaging studies, to accurately diagnose rectal prolapse and recommend appropriate treatment options.
How is Rectal Prolapse Diagnosed?
Diagnosing rectal prolapse involves a thorough examination, including:
Medical History
Gathering information about symptoms and risk factors.
Physical Examination
Our colorectal specialists may conduct a rectal examination to assess the extent of the prolapse.
Imaging Studies
Procedures such as colonoscopy or rigid sigmoidoscopy may be recommended to visualize the rectum and assess the severity of the prolapse.
Timely diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment. While mild cases may be managed with lifestyle modifications and pelvic floor exercises, more severe cases may require surgical intervention to reposition and secure the rectum.
Rectal prolapse is a condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, but with prompt and appropriate care, effective management is possible. If you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms of rectal prolapse, seeking medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan is essential. Midlands Colorectal is dedicated to providing expert care and support for individuals facing rectal prolapse, prioritizing your health and well-being at every step of the journey.
Can Rectal Prolapse Be Prevented?
While certain risk factors for rectal prolapse, such as age and genetics, are beyond one's control, there are preventive measures and lifestyle changes that individuals can adopt to reduce the risk of developing or exacerbating rectal prolapse. Here's a closer look at strategies for prevention:
Maintain a High-Fibre Diet
A diet rich in fibre promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation, which is a significant contributing factor to rectal prolapse. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your daily diet. These fibre-rich foods add bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass.
Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining soft and formed stools, reducing the need for straining during bowel movements. Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Aim for at least two litres of water daily.
Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegel Exercises)
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help support the rectum and prevent its descent. Learn and practice Kegel exercises regularly. These exercises involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles.
Avoid Straining During Bowel Movements
Straining during bowel movements can weaken the pelvic floor muscles and contribute to the development of rectal prolapse. If a bowel movement is difficult, consider making dietary adjustments or seeking guidance from a healthcare professional. Ensure a high-fibre diet, stay hydrated, and establish a regular bowel routine to minimize the need for straining.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can place additional strain on the pelvic floor muscles, increasing the risk of prolapse. Adopt a healthy and balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and manage body weight within a healthy range.
Proper Lifting Techniques
Incorrect lifting techniques can strain the pelvic floor and contribute to prolapse. Lift heavy objects using your legs, not your back. Avoid holding your breath during lifting.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity promotes overall health, including the strength of pelvic floor muscles and the prevention of constipation. Engage in moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Timely Treatment of Constipation
Chronic constipation is a significant risk factor for rectal prolapse. If constipation is a recurring issue, seek medical advice for appropriate management and treatment.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular health check-ups allow for the early detection and management of conditions that may contribute to rectal prolapse. Schedule routine appointments with your healthcare provider to address any concerns and discuss preventive measures.
What Are the Treatment Options for Rectal Prolapse?
The treatment approach for rectal prolapse depends on the severity of symptoms, the type of prolapse, and the overall health of the individual. Treatment options range from non-surgical interventions to surgical procedures. Here's an in-depth look at the various treatment options for rectal prolapse:
Non-Surgical Approaches
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
Addressing contributing factors such as constipation by increasing fibre intake, maintaining hydration, and establishing a regular bowel routine can alleviate symptoms.
Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegel Exercises)
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles will provide better support. Regular practice of Kegel exercises can improve muscle tone and reduce the risk of prolapse.
Surgical Interventions
Rectopexy
Surgical fixation of the rectum with a rectopexy will provide support and prevent prolapse. It can be performed through an abdominal approach (abdominal rectopexy) or a perineal approach (perineal rectopexy).
Delorme's Procedure
This involves partial removal of the rectal lining to correct mucosal prolapse. Performed through the perineum, it is suitable for specific cases of rectal prolapse.
Altemeier Procedure
In this procedure rectal prolapse is corrected through a perineal approach with rectal resection. It involves removing the prolapsed rectum and then reattaching it to the anus.
Colostomy
A colostomy helps by redirecting the bowel to bypass the prolapsed segment. A surgical opening is created in the abdominal wall for stool elimination.
Other Procedures
Transanal Irrigation
Using a catheter to instil fluid into the rectum, facilitating bowel movements to manage bowel function can be used in selected cases.
Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS)
An implantable device delivers electrical stimulation to the sacral nerves, influencing bowel function and modulating nerves to improve bowel control.
Dynamic Graciloplasty
Utilizing muscle tissue to enhance anal sphincter function to reconstuct the anal sphincter using muscle grafts.
Perianal Injectable Bulking Agents
Improving anal sphincter function to reduce prolapse by injecting bulking agents to augment tissue and provide additional support.
It's crucial to note that the choice of treatment depends on the individual's condition, preferences, and overall health. A thorough evaluation by a colorectal specialist, such as those at Midlands Colorectal, is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Treatment decisions are made collaboratively, considering the individual's goals and expectations. Regular follow-ups and ongoing communication with the healthcare team are integral parts of managing rectal prolapse effectively.
What is the Recovery Process After Rectal Prolapse Surgery?
The recovery process after rectal prolapse surgery varies depending on the type of surgical procedure performed, the extent of the prolapse, and individual factors such as overall health and adherence to postoperative guidelines. Here's an overview of what individuals can generally expect during the recovery period:
Postoperative Care
The length of the hospital stay depends on the type of surgery and individual factors. Vital signs and postoperative recovery will be closely monitored. Pain medication will be prescribed to manage discomfort. Pain levels and medication effectiveness will be monitored by the healthcare team.
Individuals should be aware of potential complications, such as infection, bleeding, or changes in bowel function. Detailed instructions on incision care, including cleaning and dressing changes. The healthcare team will monitor the incision site for signs of infection or complications.
Dietary Adjustments
The reintroduction of solid foods is typically gradual, starting with liquids and progressing to a soft diet. Dietary recommendations will be provided by the healthcare team to promote optimal healing.
Physical Activity and Movement
The resumption of normal activities is gradual and depends on individual recovery. Temporary restrictions on heavy lifting or strenuous activities may be advised. Specific instructions on when to resume activities, including exercise, will be provided.
Recommendations on when it is safe to resume work and social activities will be based on the nature of the individual's occupation and lifestyle.
Follow-Up Appointments & Ongoing Monitoring
Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare team will be arranged to monitor recovery progress. Physical examinations and potentially imaging studies to assess surgical outcomes. Patients should be vigilant for any signs of recurrence of rectal prolapse. Prompt reporting of any unusual symptoms or concerns to the healthcare team is vital.
Adhering to postoperative guidelines and instructions is crucial for a successful recovery. Understanding the recovery process will prepare patients for a smoother postoperative experience and the above guidelines provide a general overview. Midlands Colorectal is committed to supporting individuals throughout their recovery, providing personalised care, and addressing any concerns or questions that may arise during the postoperative period. Open communication and collaboration with the healthcare team are key elements in ensuring a smooth and successful recovery journey.
How Can Midlands Colorectal Help Individuals with Rectal Prolapse?
At Midlands Colorectal, we prioritize your health and are dedicated to guiding you through every step of the diagnosis and treatment process.
Our team can help connect patients with Support Groups, Connecting with others experiencing similar challenges. Midlands Colorectal recognise the importance of emotional support and will provide information on these resources.
Rectal prolapse is a complex condition that requires understanding, prompt diagnosis, and personalized care. Midlands Colorectal is committed to providing the expertise and support needed for individuals facing rectal prolapse. If you have concerns or symptoms related to rectal prolapse, we are here to guide you through accurate diagnosis and comprehensive treatment options, ensuring your